-
Xi Khoe Trading - Energy Solutions with Natural Gas and Gas Turbine Technologies
Providing sustainable energy solutions using the availability of natural gas and gas turbine technology for power plants ensuring efficient, reliable and eco-friendly power generation for today.
Let’s build a cleaner, more resilient energy future together!
-
Over the past few decades, South Africa's electricity demand has increased, and its national generation capacity has been unable to keep up with the rising demand due to a decaying infrastructure. The country's power system primarily relies on aging coal-fired power generation stations that are no longer able to provide sufficient electricity, resulting in an unreliable power supply. In addition, the use of fossil fuels for energy generation has contributed to greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating climate change concerns. To address these issues, more efficient and cleaner energy solutions need to be implemented.
South Africa has been exploring natural gas fields along its southwest coast and in other parts of the country, offering a unique opportunity to develop alternative fuel sources for power stations. The country has already built a number of dual-fuel gas power stations, but they burn diesel or paraffin, which makes them expensive to operate.
Advancements in engine technology and changes in natural gas markets have driven the recent increase in natural gas or dual-fuel capable reciprocating internal combustion engine units. Additionally, recent amendments to government regulations have extended licensing exemptions and registrations allowing industries, mines, municipalities, and other users to reduce reliance on the national grid and alleviate pressure on the national supplier.
Over the past few decades, South Africa's electricity demand has increased, and its national generation capacity has been unable to keep up with the rising demand due to a decaying infrastructure. The country's power system primarily relies on aging coal-fired power generation stations that are no longer able to provide sufficient electricity, resulting in an unreliable power supply. In addition, the use of fossil fuels for energy generation has contributed to greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating climate change concerns. To address these issues, more efficient and cleaner energy solutions need to be implemented.
South Africa has been exploring natural gas fields along its southwest coast and in other parts of the country, offering a unique opportunity to develop alternative fuel sources for power stations. The country has already built a number of dual-fuel gas power stations, but they burn diesel or paraffin, which makes them expensive to operate.
Advancements in engine technology and changes in natural gas markets have driven the recent increase in natural gas or dual-fuel capable reciprocating internal combustion engine units. Additionally, recent amendments to government regulations have extended licensing exemptions and registrations allowing industries, mines, municipalities, and other users to reduce reliance on the national grid and alleviate pressure on the national supplier.
-
Powering with Gas
Natural gas and gas turbine technology for efficient and sustainable power generation. The transition solution now.
-
Clean and Reliable
Small physical footprint and minimised impact on the environment. Always available.
-
Flexible and Efficient
Designed for specific solutions and applications. Easily adapted to various power demands.
-
Affordable and Cheaper
Increased affordability and new ownership models! Reduced costs.
-
Transition and Hybrids
Faster local and micro-grid tie-ins. Peaking and hybrid solutions now. Out-of-the-box switch on!
-
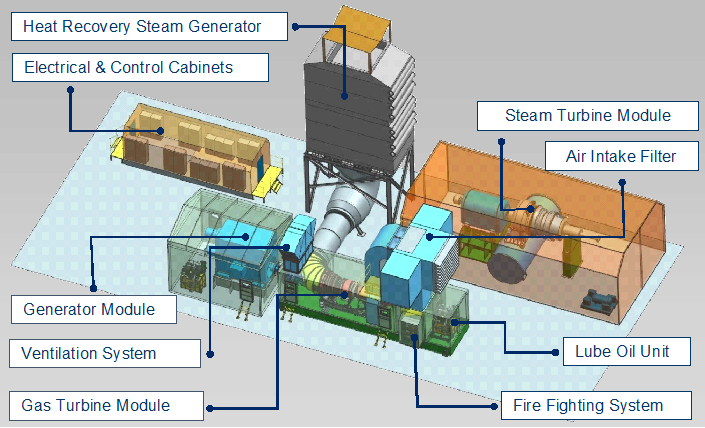
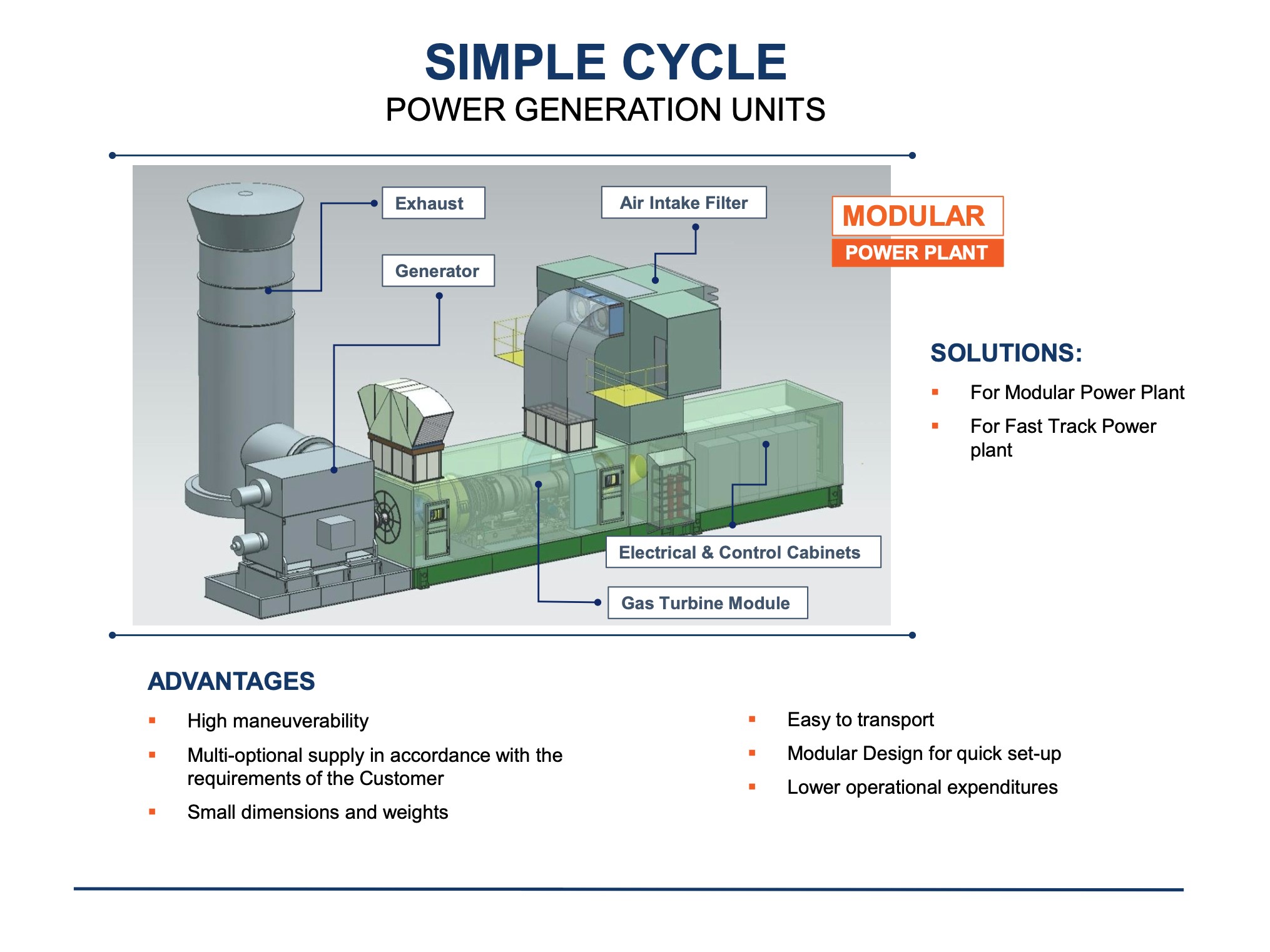
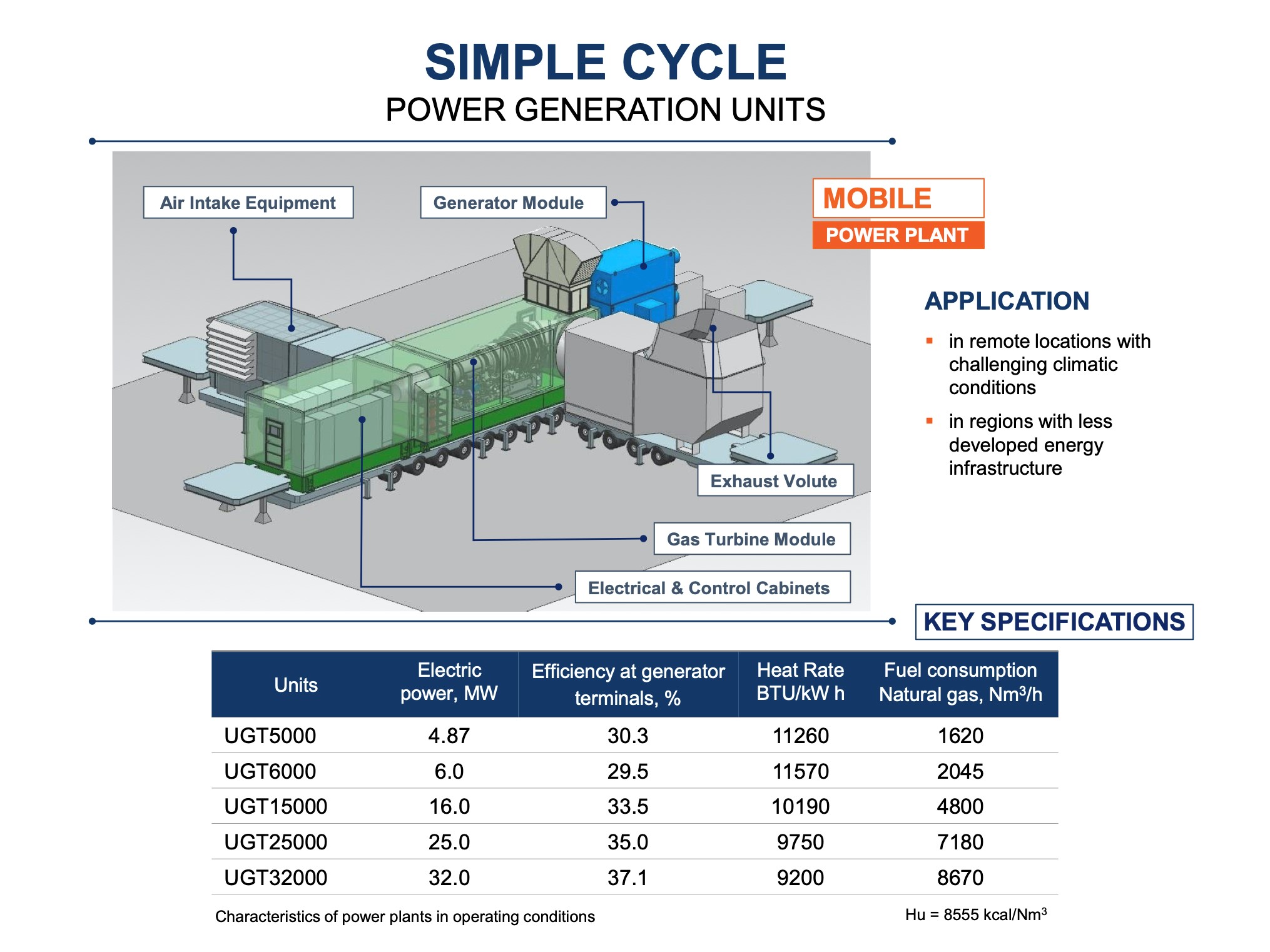
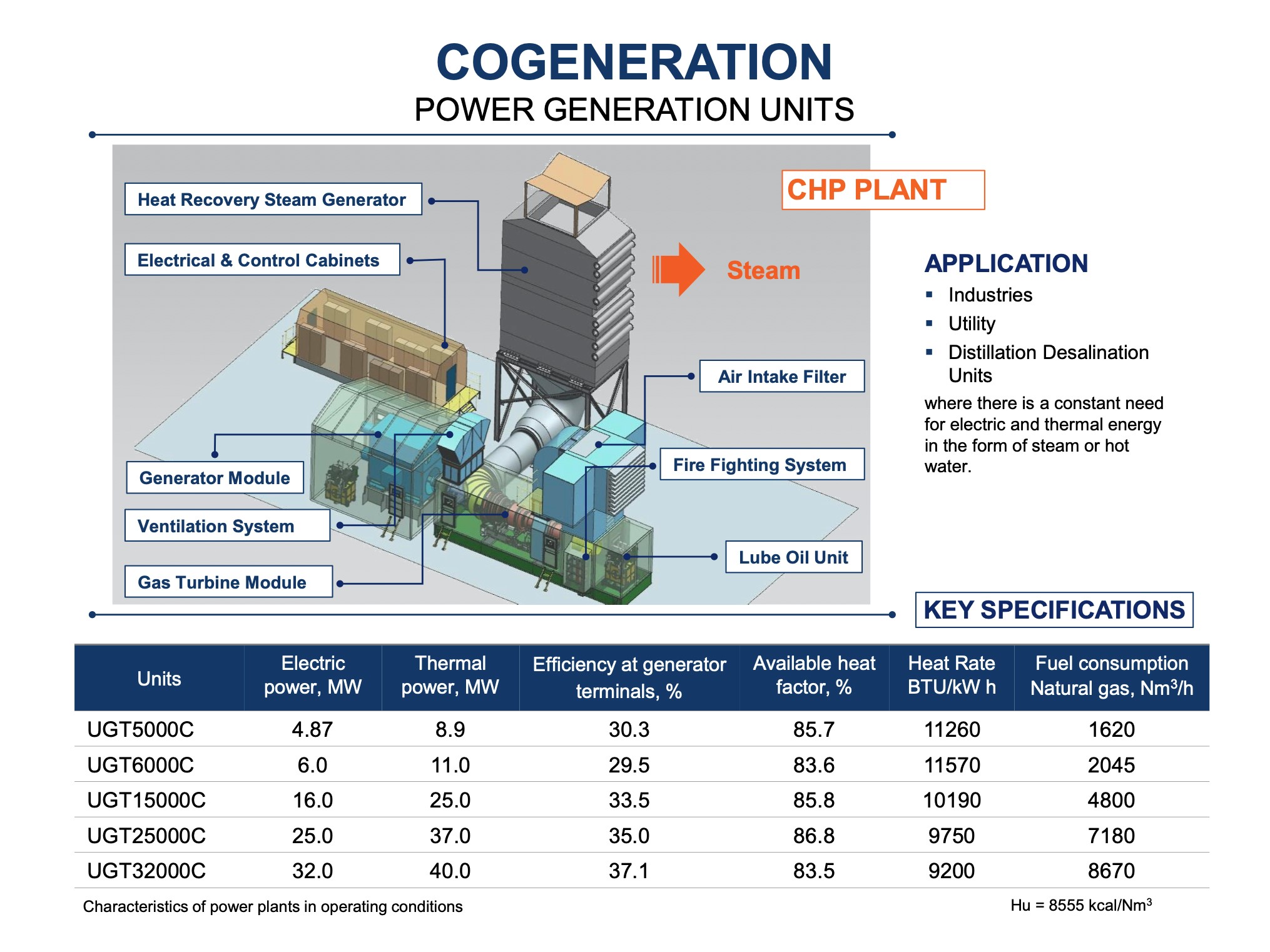
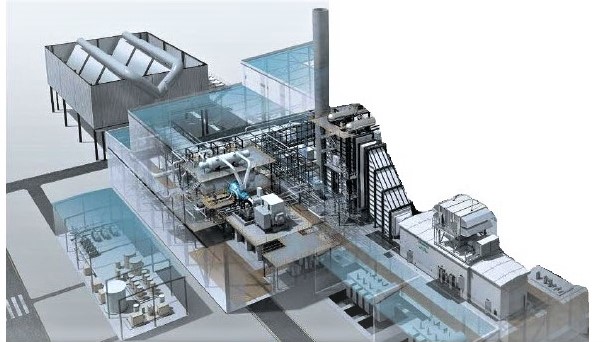
Choose the PLANT that suits your needs:
We offer flexible solutions to meet the energy requirements of industries and municipalities in South Africa where natural gas is available:
- Turnaround times from 12 - 18 months for plant construction
- (after all government approvals,
- grid connection approvals,
- gas tie-in and possible additional pipeline & compressor stations
- environmental assessments and approvals)
- NERSA approval not required for plants up to 100 Mw
- Pollution and environmental impact reduction measures and options
- noise reduction through dampening
- air filtering and scrubbing
- hydrogen production from emissions
- Combined cycle gas generation
- steam / heat
- power for other industrial processes
- water desalination
- Dual fuel use
- Conversion of existing plants
- Hybrid plants
- Turnaround times from 12 - 18 months for plant construction
Options for selecting a Gas Power Plant
Ideal for small industries and municipalities
- Up to 10 MW power capacity
- 24/7 customer support
- Regular maintenance and servicing
- Flexible contract terms
- Access to local micro grids
- 6 500 homes can be powered
Perfect for medium-sized industries, mining and municipalities
- Up to 25 MW power capacity
- 24/7 customer support
- Regular maintenance and servicing
- Flexible contract terms
- Access to local micro grids
- 16 250 homes can be powered
Designed for large industries, mines and municipalities
- 50 - 100 Mw power capacity
- 24/7 customer support
- Regular maintenance and servicing
- Flexible contract terms
- Access to local micro grids
- Power for 65 000 homes!
Designed for national grids, large industrial hubs , mines and municipalities and metros
- Requires NERSA approval
- From 100 Mw and above power capacity
- 24/7 customer support
- Regular maintenance and servicing
- Interim and transition power solution
- Access to local micro grids and national grid
- Power for cities, towns and provinces
Frequently Asked Questions
Natural gas is a fossil fuel formed deep underground from the remains of ancient plants and microorganisms.
It’s primarily composed of methane (CH₄) but also contains small amounts of ethane, propane, and other gases. It’s considered a cleaner-burning energy source compared to coal or oil, producing fewer greenhouse gases and pollutants when burned. Natural gas is odourless, so a sulphur-like smell is added for safety to detect leaks.
Natural gas is versatile and supports a wide range of energy needs:
- Electricity Generation: Power plants use gas turbines or combined-cycle systems to produce electricity efficiently.
- Heating: Homes and businesses use it for heating spaces and water.
- Industrial Processes: Provides high-temperature heat for manufacturing (e.g., steel, chemicals, and cement).
- Transportation: Compressed natural gas (CNG) fuels buses, trucks, and ships.
- Combined Heat and Power (CHP): Captures waste heat from electricity generation to improve overall efficiency (up to 90%).
- Lower Emissions: Produces ~50% less CO₂ than coal and fewer pollutants (e.g., sulphur dioxide, particulates).
- High Efficiency: Modern combined-cycle plants achieve 60%+ efficiency, converting more fuel into electricity.
- Flexibility: Gas turbines ramp up/down quickly, balancing grids with renewable energy (e.g., solar/wind).
- Reliability: Less prone to outages than weather-dependent renewables.
Cost-Effective: Abundant supply and lower infrastructure costs compared to coal or nuclear
Gas turbines are engines that convert fuel into mechanical energy via combustion. Here’s how they work:
- Air is compressed and mixed with fuel (e.g., natural gas).
- The mixture ignites, creating hot, expanding gases.
- These gases spin turbine blades, driving a generator to produce electricity.
Gas turbines are used in power plants, aviation, and industrial settings. Types include aeroderivative (lightweight, fast-start) and heavy-duty (high-capacity).
While natural gas is the most common fuel, gas turbines can also run on:
- Liquid Fuels: Diesel, kerosene.
- Alternative Gases: Hydrogen blends, biogas (from waste), or syngas.
- Dual-Fuel Systems: Switch between gas and liquid fuels for flexibility.
Note: Fuel choice impacts efficiency, emissions, and maintenance.
Yes! Modern gas turbines excel in efficiency:
- Simple-Cycle Efficiency: ~35–40% (electricity-only).
- Combined-Cycle Efficiency: Up to 60%+ by reusing waste heat to power a steam turbine.
- CHP Systems: Reach 80–90% efficiency by also using heat for buildings/industries.
They’re ideal for peak demand and grid stability due to rapid response times (minutes vs. hours for coal plants).
Micro grids are localized power grids that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main power grid. They contribute to offsetting energy challenges by providing reliable and efficient energy solutions to industries and municipalities in areas where natural gas is available.
Microgrids are localized energy networks that can operate independently or alongside the main grid. They combine:
- Distributed Energy Sources: Solar panels, wind turbines, natural gas generators.
- Storage: Batteries or thermal storage.
- Smart Controls: Balance supply and demand in real-time.
Benefits:
- Resilience: Provide backup power during outages or disasters.
- Renewable Integration: Store excess solar/wind energy for later use.
- Reduce Transmission Losses: Generate power closer to where it’s needed.
- Energy Access: Power remote or off-grid communities.
Industries:
- Reliable Power: Avoid costly downtime with on-site gas turbines or microgrids.
- Cost Savings: Use CHP to cut energy bills by recycling waste heat.
- Lower Emissions: Meet sustainability goals with cleaner gas turbines vs. coal/diesel.
Municipalities:
- Grid Stability: Gas turbines balance intermittent renewables in microgrids.
- Emergency Readiness: Microgrids keep hospitals, schools, and critical services running during outages.
- Economic Growth: Reliable energy attracts businesses and supports local jobs.
- Sustainability: Pair gas turbines with renewables for a low-carbon transition.